Correlation Analysis between Conservative and Liberal
Indexes
1.
Summaries
of Previous Analysis
In COVID-19 data analysis 4 series, we
have observed whether global citizens prefer conservative values or liberal ideas
amid COVID-19 pandemic. There are seven different groups of indexes, which are
divided by conservative and liberal perspectives. Generally speaking, a conservative
ideology puts an emphasis on rules, order, and social stability; contrarily,
liberal values stress on individual rights and liberties. Accordingly, in this
data analysis series, conservative indexes consist of Disaster Weathering
Priority Index (DWPI), Health Priority Index (HPI), Government Decisions Index
(GDI), Rule by Order Index (ROI), Leadership-centered Disinfection Index (LDI),
Government-centered Quarantine Index (GQI), and Data Transparency Index (DTI).
Correspondingly, indexes which hold liberal values include Civil Liberties
Priority Index (CLPI), Economy Priority Index (EPI), Citizens Requests Index
(CRI), Rule of Law Index (RLI), Cooperation-centered Disinfection Index (CDI), Citizen-centered
Quarantine Index (CQI), and Data Privacy Index (DPI).
The data analyses demonstrate that there
is a general trend in the world in the course of COVID-19 crisis. Except for a
small number of cities, most cities are in line with the same position in
different questions in the questionnaire. For example, the survey result shows
that all 30 cities believe that weathering the disaster should be prioritized
instead of civil liberties during the COVID-19. Also, without Moscow, all
cities tend to put a priority on public health rather than economic recovery. Moreover,
most cities were inclined to follow the government’s decisions than listen to
public opinion. In sum, overall global citizens are likely to hold conservative
values to mitigate the surge of the COVID-19. The grey parts in Table 1 indicate
that the corresponding values are underlined by global citizens and those
cities which are not for those ideas are listed below the indexes.
However, global citizens also highlight
liberal values simultaneously. For instance, people believe that the value of
rule of law should not be diminished even during an urgent situation. Besides, most
of the global citizens conceive that slowing the transmission of the disease
requires citizens’ cooperation, as explained in “data analysis 4.5” and “data
analysis 4.6”. In conclusion, global citizens put importance on government
decisions to secure public health, but they hold that citizens’ cooperation and
participation are of great significance, and the government’s efforts may be useless
without people’s collaboration in containing COVID-19 epidemics. Meanwhile, there
are contradicting views on data transparency and data privacy, implying that
the privacy issue is highly controversial in international society.
Table 1: Comparison of Conservative and Liberal Indexes among 30 global cities 2.
Methodology
and Hypothesis In this section, we cross-checked
different indexes for identifying if there is a correlation between the items related
to conservative and liberal values. The independent variable is the Citizen
Requests Index (CRI) that varies from 1 to 10, where 1 is sharing the least
liberal identity and 10 is having the most liberal ideas. The dependent
variables are the other six indexes, including Civil Liberties Priority Index
(CLPI), Economy Priority Index (EPI), Rule of Law Index (RLI),
Cooperation-centered Disinfection Index (CDI), Citizen-centered Quarantine
Index (CQI), and Data Privacy Index (DPI). All of these indexes’ scaling is the
same as the independent variable. We hypothesize that people who have higher
requirements on citizens’ requests, they prioritize liberal values, such as
civil liberties, economic recovery, rule of law, citizen-centered quarantine,
cooperation among citizens, and data privacy. Because of the clear
directionality of the hypotheses in this analysis, we perform one-tailed
hypothesis tests. 3.
Major
Outcomes The table
indicates the relationship between requirements for citizens’ requests and
other liberal values. Consistent with the argument that people with higher
requirements for citizens’ requests share more individual and liberal ideas. Figure 1: Correlation Between Citizen Requests Index
(CRI) and Civil Liberties Priority Index (CLPI) Figure 1 shows the
relationship between Citizen Requests Index and Civil Liberties Priority Index.
The positive slope indicates that the two indexes are positively related, which
means that people who ask for citizens’ requests than government decisions prioritize
civil liberties than overcoming the disaster. Figure 2: Correlation Between Citizen Requests Index
(CRI) and Economy Priority Index (EPI) Figure 2 shows the
relationship between Citizen Requests Index and Economy Priority Index. The
positive slope indicates that the two indexes are positively related, which
means that people who ask for citizens’ requests than government decisions
prioritize economic recovery than public health protection. Figure 3: Correlation Between Citizen Requests Index
(CRI) and Rule of Law Index (RLI) Figure 3 shows the
relationship between Citizen Requests Index and Rule of Law Index.
The positive slope indicates that the two indexes are positively related, which
means that people who ask for citizens’ requests than government decisions put
more emphasis on rule of law. Figure 4: Correlation Between Citizen Requests Index (CRI) and Cooperation-centered Disinfection Index (CDI) Figure 4 shows the
relationship between Citizen Requests Index and Civil Liberties Priority Index.
The positive slope indicates that the two indexes are positively related, which
means that people who ask for citizens’ requests than government decisions stress
on cooperation in society than the government’s leadership. Figure 5: Correlation Between Citizen Requests Index (CRI) and Citizen-centered Quarantine Index (CQI) Figure 5 shows the
relationship between Citizen Requests Index and Civil Liberties Priority Index.
The positive slope indicates that the two indexes are positively related, which
means that people who ask for citizens’ requests than government decisions believe
that the citizens are the main actor in the prevention of an epidemic. Figure 6: Correlation Between Citizen Requests Index
(CRI) and Data Privacy Index (DPI) 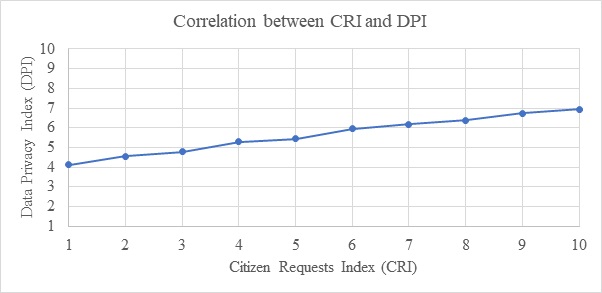 Figure 6 shows the
relationship between Citizen Requests Index and Civil Liberties Priority Index.
The positive slope indicates that the two indexes are positively related, which
means that people who ask for citizens’ requests than government decisions advocate
data privacy and individual rights.
These are the
general trends in global cities amid COVID-19; however, more specific data analysis
is demanded to further understand the phenomena in different cities and
countries.
|